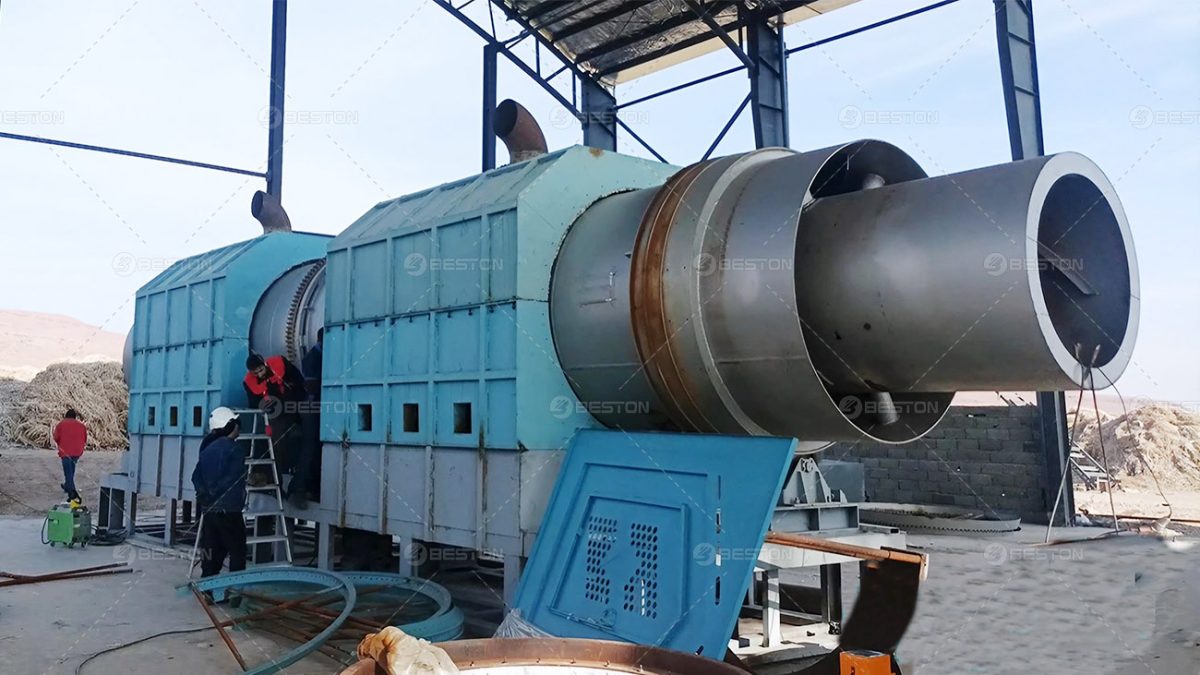
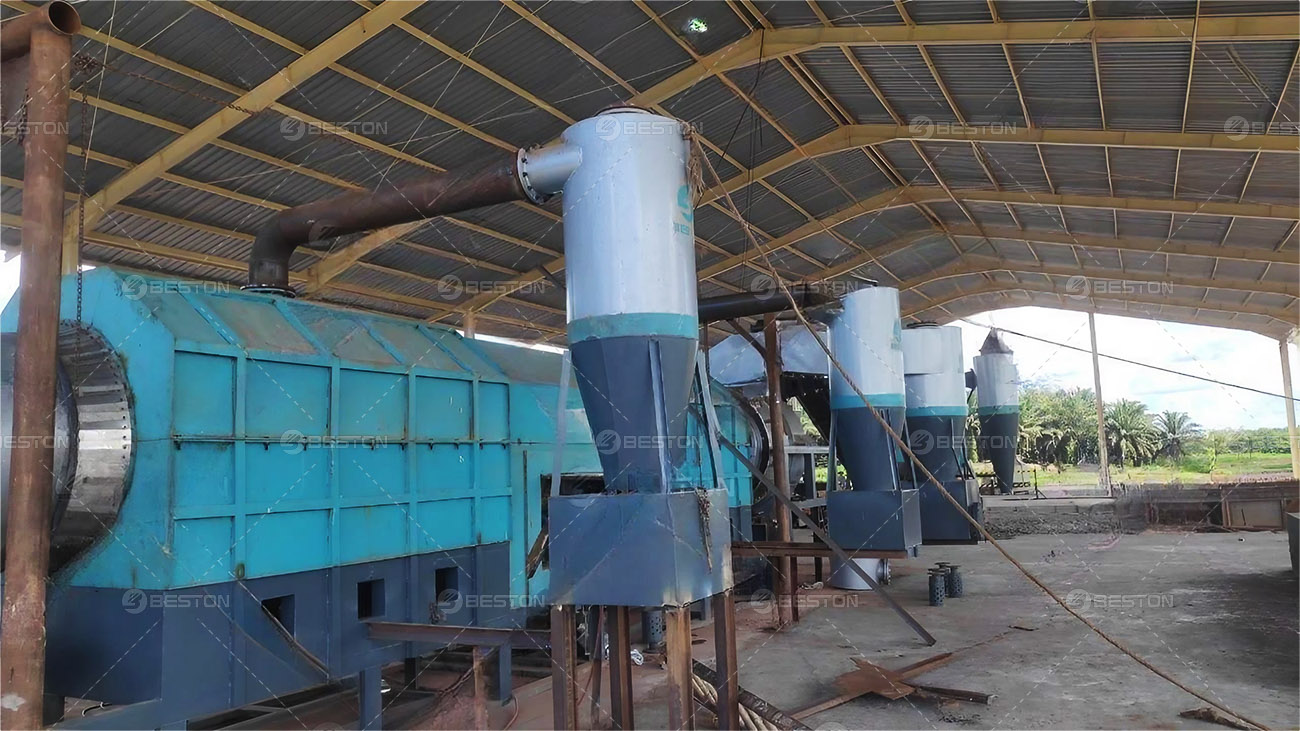
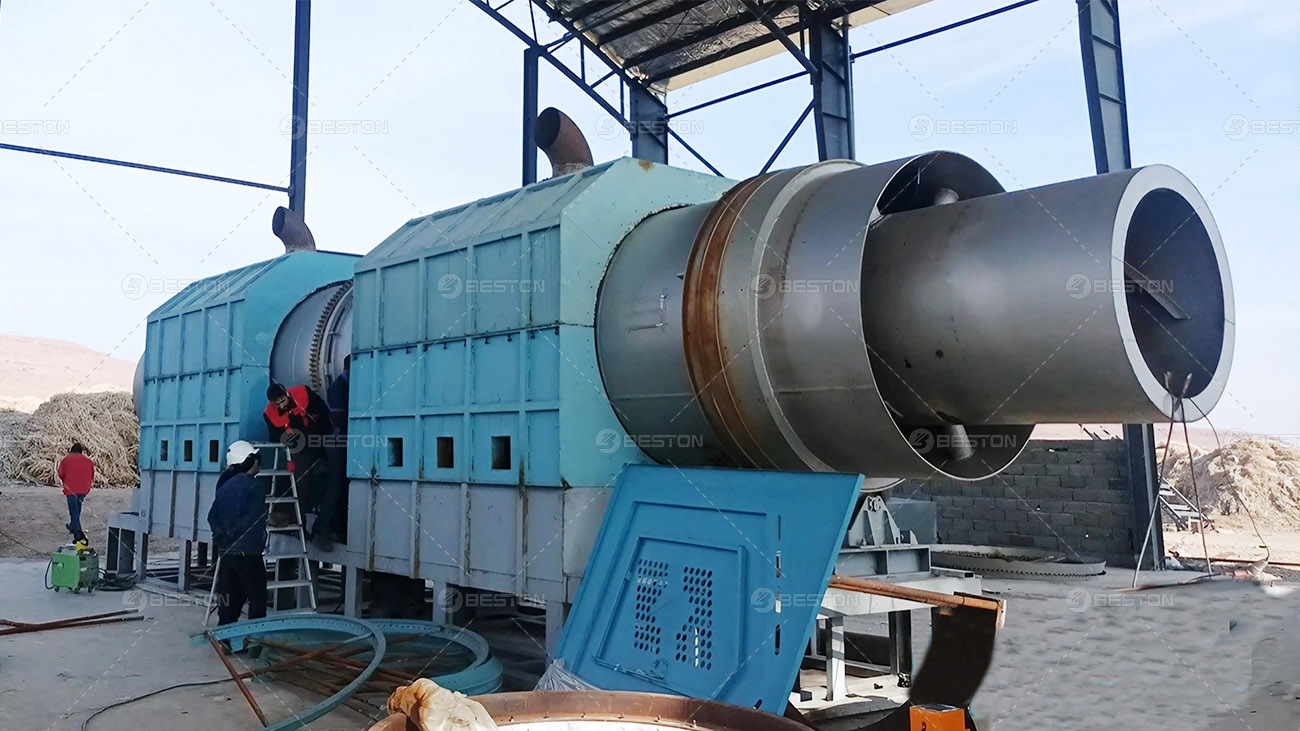
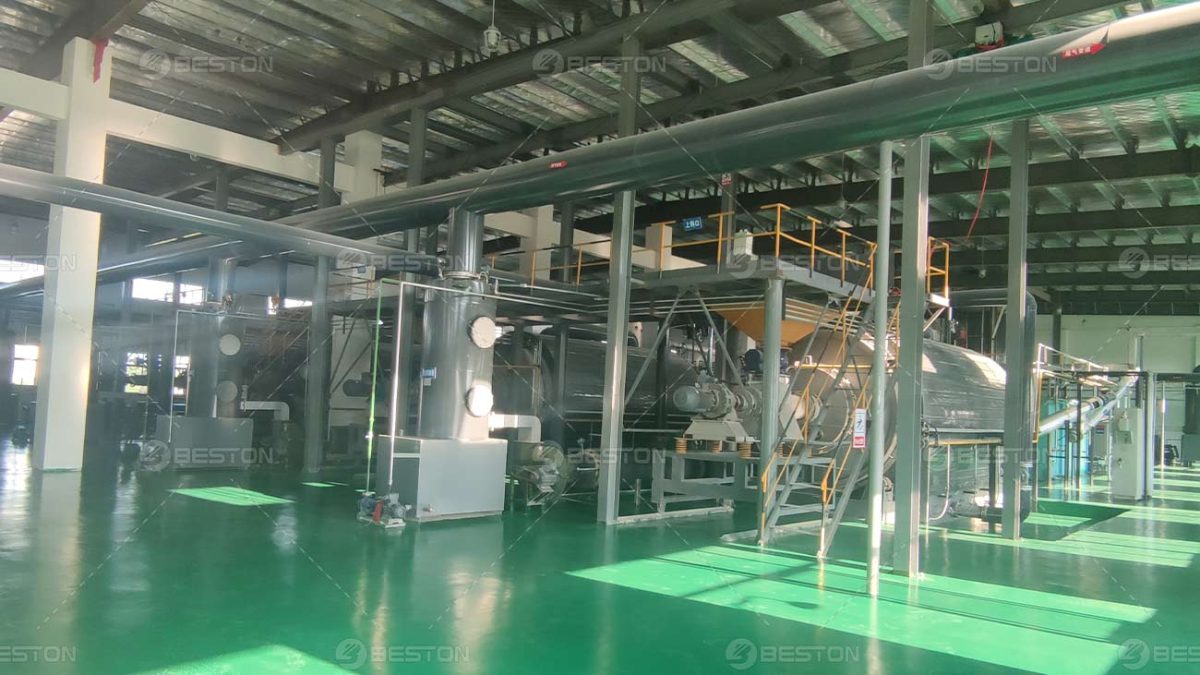
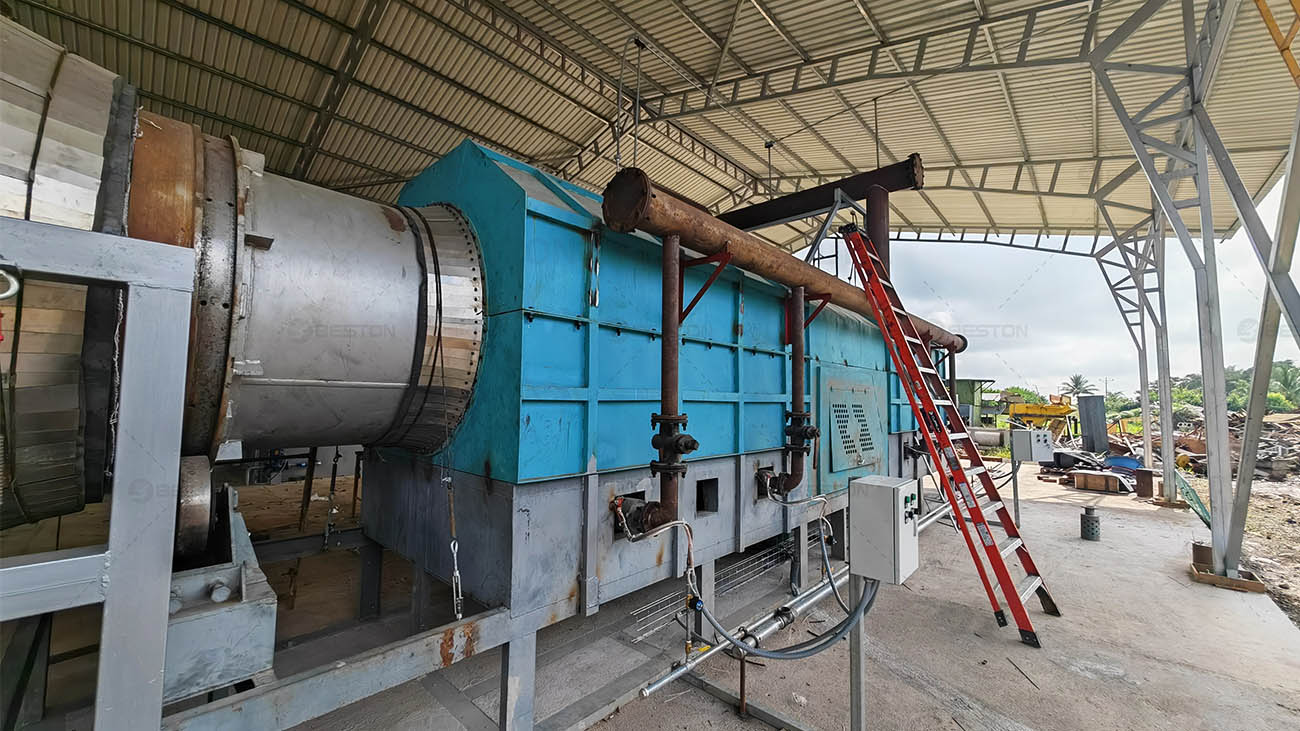
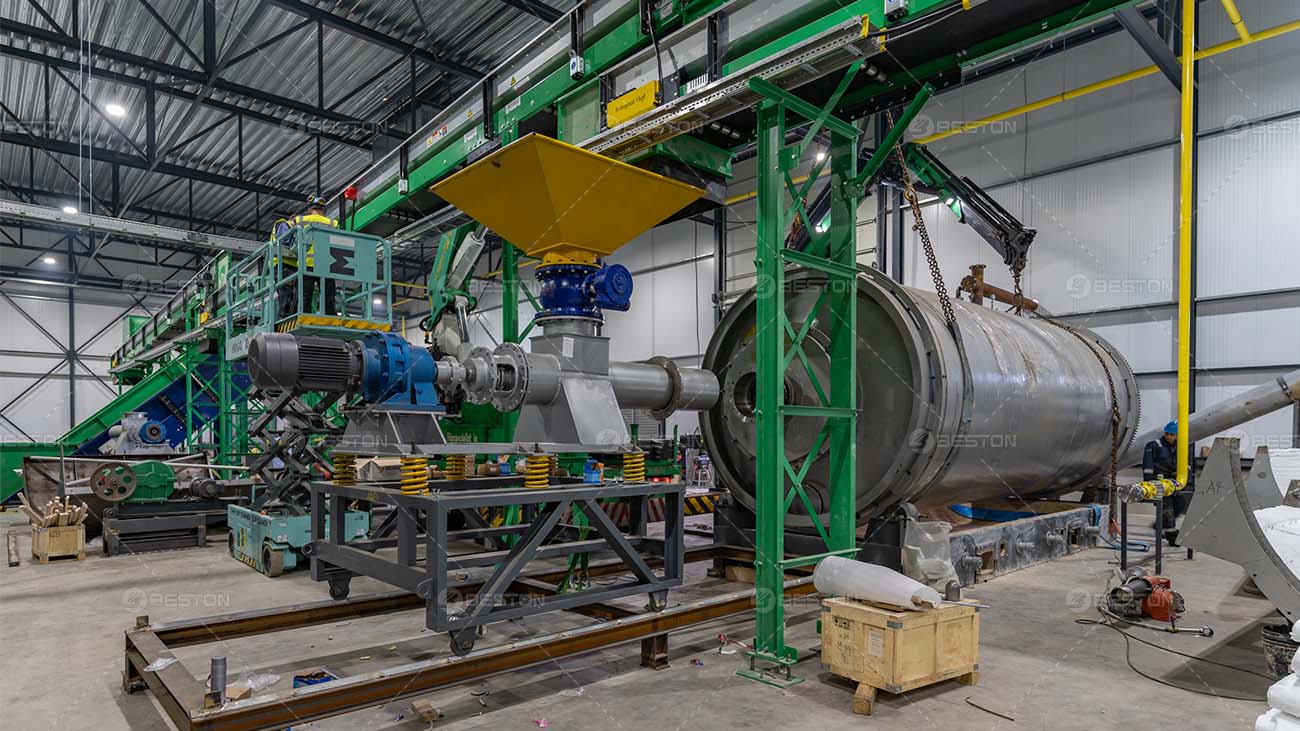
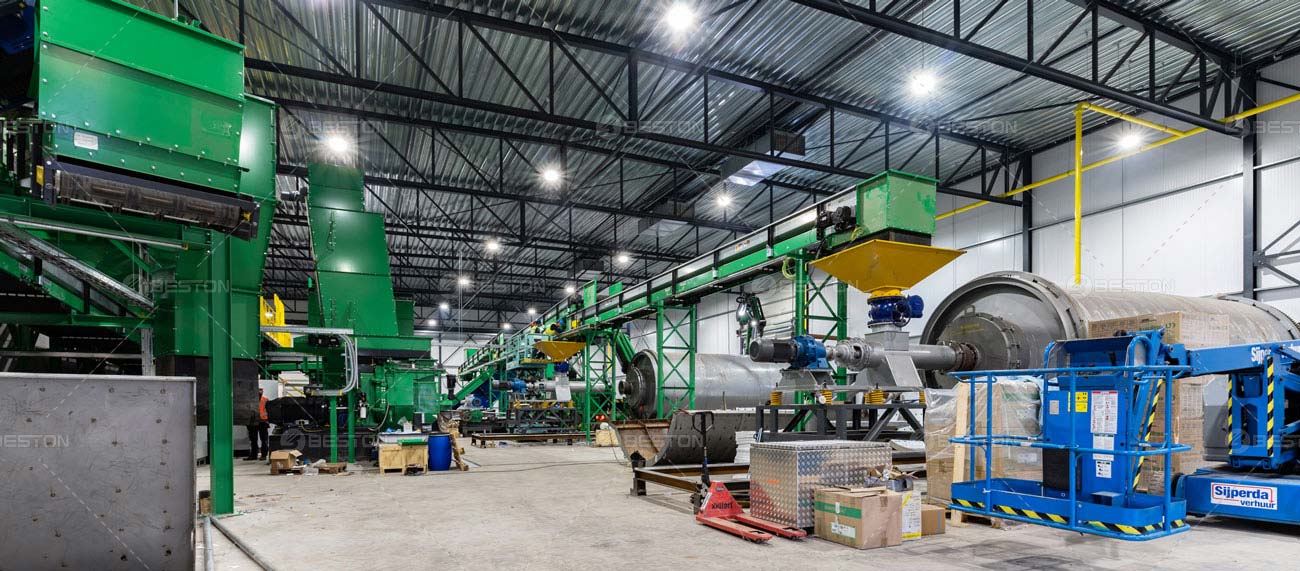
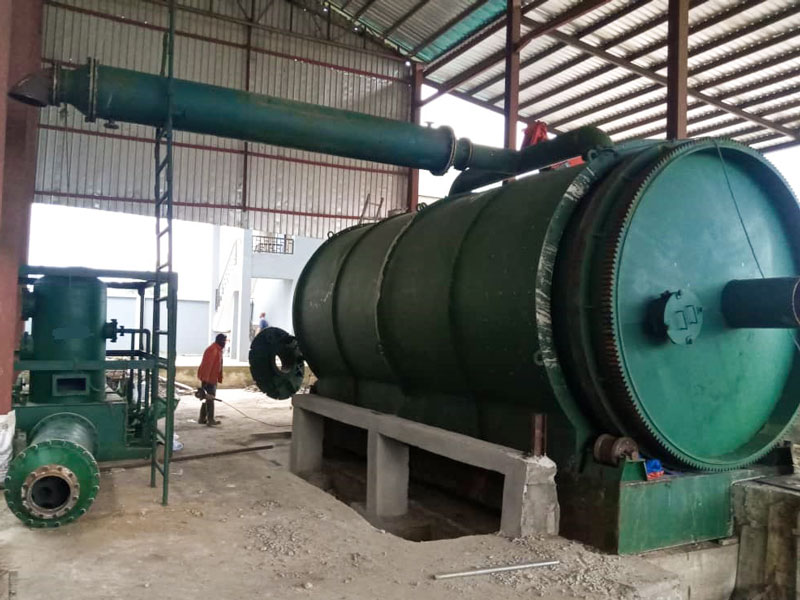
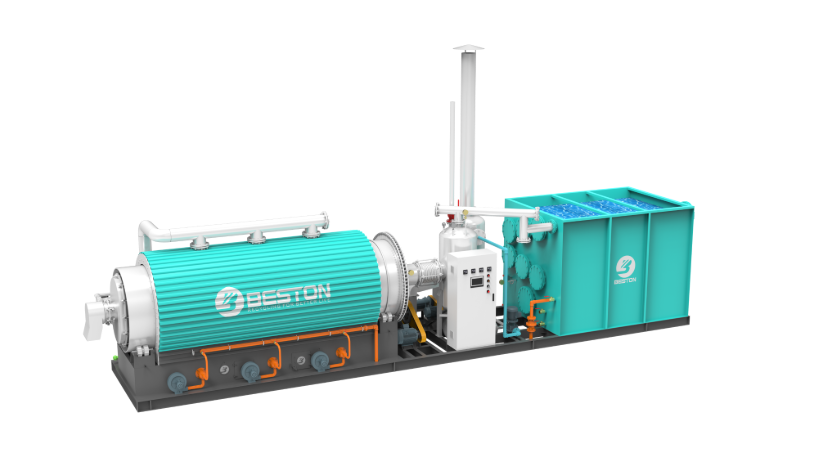
The growing urgency to transition from fossil-based systems to renewable energy frameworks has accelerated interest in alternative waste-to-fuel technologies. A pyrolysis plant occupies a strategic position in this transition, offering a means to convert persistent waste streams into usable fuels and carbonaceous by-products. Its integration with renewable energy strategies not only reduces dependency on non-renewable resources but also addresses the escalating global challenge of plastic waste.
Linking Waste Conversion with Energy Security
Energy security relies on diversified and resilient supply channels. A waste plastic pyrolysis machine transforms discarded polymers into pyrolytic oil and syngas, both of which can serve as substitutes for conventional fuels in power generation and industrial applications. These outputs align with renewable energy strategies by supplementing intermittent sources like solar or wind, ensuring stable and reliable energy access. Through distributed deployment, small plastic pyrolysis machine units further extend these benefits to localized waste management and energy generation systems.
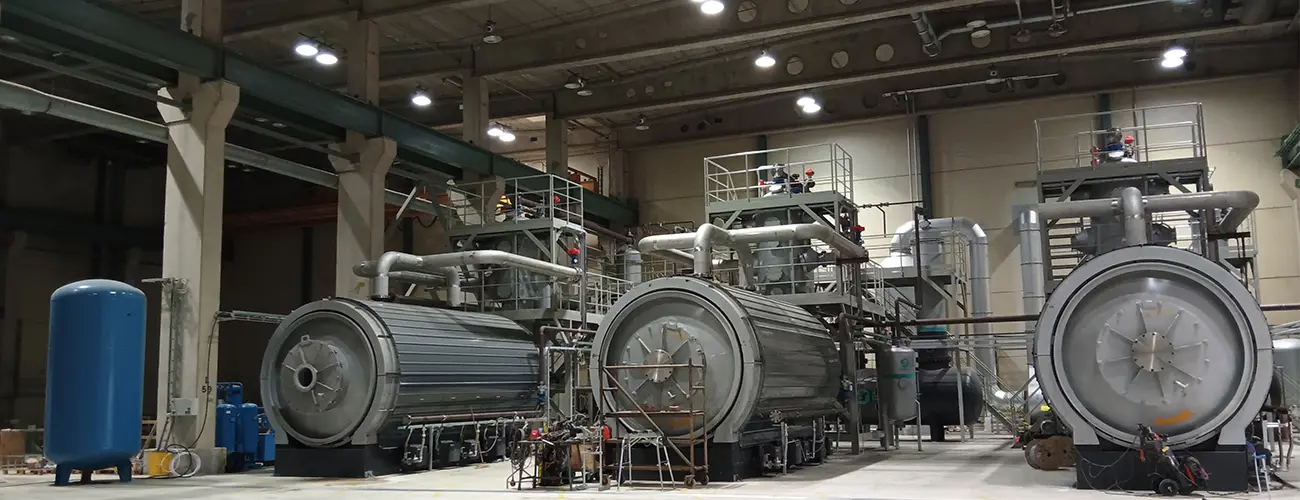

Expanding the Role of Waste-to-Fuel Systems
Plastic waste represents a formidable challenge for modern societies, given its resistance to degradation and limited recycling pathways. A waste plastic to fuel machine for sale embodies a practical response, converting mixed and contaminated feedstocks into valuable resources that reintegrate into the economic cycle. The resulting oil can be refined for transport applications or blended with renewable fuels, advancing the broader agenda of reducing greenhouse gas emissions while extending resource lifecycles.

Supporting Renewable Energy Infrastructure
Waste plastic pyrolysis machine operate in synergy with renewable infrastructure by providing baseline energy solutions during periods of low renewable output. Syngas generated within the process can be utilized directly to sustain plant operations, reducing external energy requirements. Excess energy can be channeled into microgrids, complementing renewable installations in both rural and industrial settings. This interplay enhances the resilience of renewable energy systems, reinforcing their role in long-term decarbonization strategies.
Environmental Performance and Policy Alignment
The shift from uncontrolled plastic disposal toward structured thermochemical conversion reduces emissions and mitigates environmental contamination. Pyrolytic processes minimize the release of harmful compounds while diverting plastics from landfills and waterways. Such performance resonates with global policies that emphasize waste valorization and renewable integration. Pyrolysis plant suppliers are now adapting their systems to comply with stricter emission standards, ensuring compatibility with sustainable energy frameworks.
Economic and Industrial Implications
The integration of pyrolysis plants into renewable energy strategies generates significant industrial value. Recovered fuels lower operational costs, while carbon black by-products create new market opportunities in construction and manufacturing. Furthermore, the deployment of waste plastic pyrolysis machine technology stimulates local job creation in collection, processing, and distribution. By closing resource loops and reducing reliance on virgin petrochemicals, these systems support both economic development and environmental stewardship.
Future Trajectory
As renewable energy strategies evolve, the role of pyrolysis will expand through advancements in automation, feedstock flexibility, and integration with carbon capture technologies. Pyrolysis plant suppliers are expected to deliver increasingly sophisticated solutions that merge waste conversion with energy innovation. Positioned at the intersection of waste management and renewable integration, the technology exemplifies a decisive step toward building sustainable, circular, and resilient energy systems worldwide.